T2I Models Explained,
STF
A Stable Target Field (STF) objective is proposed as a generalized version of the denoising score-matching objective to reduce the variance of training targets using an additional reference batch of examples.
Model Card View All Models
View All Models 
100+ Technical Experts

50 Custom AI projects

4.8 Minimum Rating
An Overview of STF
A Stable Target Field (STF) objective is proposed as a generalized version of the denoising score-matching objective to reduce the variance of training targets using an additional reference batch of examples.
State-Of-The-Art FID of 1.90 on CIFAR-10
SOTA FID Scores
STF generative model achieved a state-of-the-art FID score of 1.90 on CIFAR-10.
The bias vanishes with increasing reference batch size
Reduced Variance
Stable targets trade bias for lower variance, and bias decreases with a larger reference batch size.
Model's new objective enhances the image quality.
Better Image Enhancement
Improvement in diffusions models' quality, stability, and training speed on multiple datasets with ODE/SDE solvers.
Blockchain Success Starts here


-
Introduction
-
Key Highlights
-
Training Details
-
Key Results
-
Business Applications
-
Model Features
-
Model Tasks
-
Fine-tuning
-
Benchmarking
-
Sample Codes
-
Limitations
-
Other LLMs
About Model
A Stable Target Field (STF) objective is proposed as a generalized version of the denoising score-matching objective to reduce the variance of training targets using an additional reference batch of examples. STF achieves state-of-the-art performance in unconditional generation and improves the stability of score-based models on CIFAR-10 and CelebA 642. The contributions include characterizing the instability of current training objectives, proposing a stable STF objective, and demonstrating its performance gain with increasing reference batch size.
Key highlights
Highlights of the STF model are:
- A generalized version of the denoising score-matching objective called the Stable Target Field (STF) objective is proposed.
- The STF objective includes an additional reference batch of examples to calculate weighted conditional scores as targets.
- Self-normalized importance sampling is applied to aggregate the contribution of each example in the reference batch to reduce the variance of training targets.
- The bias and trace-of-covariance of the STF training targets shrink to zero as the size of the reference batch increases.
- When incorporated into EDM, the STF objective achieves state-of-the-art performance on CIFAR10 unconditional generation and improves the FID/Inception scores for other variants of score-based models.
- STF enhances the stability of converged score-based models on CIFAR-10 and CelebA 642 across random seeds and accelerates the training of score-based models while obtaining comparable or better FID scores.
- The contributions include characterizing the instability of the current diffusion model's training objective, proposing a more stable STF objective, analyzing its behavior and proving its asymptotic unbiasedness, and demonstrating its performance gain with increasing reference batch size.

Training Details
Training data
The evaluation process included using two datasets: CIFAR-10, which comprises 50,000 images of various objects in 10 classes, and CelebA, which includes over 200,000 images of celebrities.


Training dataset size
They trained the diffusion models using the STF objective and compared the results with other score estimation methods.


Training Procedure
The authors did not mention the exact size of the training dataset but stated that the CIFAR-10 dataset has 50,000 training images and the CelebA dataset has 202,599 training images.


Training time and resources
The authors did not mention the exact training time, but they mentioned that STF accelerates the training of score-based models and provides comparable or better FID scores with a 3.6× speed-up for VE on CIFAR-10.


Key Results
STF enhances the stability of converged score-based models on CIFAR-10 and CelebA 642 across random seeds and accelerates the training of score-based models while obtaining comparable or better FID scores.
| Task | Dataset | Score |
| Image Generation (VE, PC) | CIFAR-10 | 2.66 |
| Image Generation (VE, RK45) | CIFAR-10 | 5.51 |
| Image Generation (VP, DDIM) | CIFAR-10 | 5.06 |
| Image Generation (VP, RK45) | CIFAR-10 | 2.99 |
| Image Generation (EDM, Heun, NCSN++) | CIFAR-10 | 1.9 |
| Image Generation (EDM, Heun, DDPM+) | CIFAR-10 | 1.92 |
| Image Generation (VE, RK45) | CelebA 64x64 | 5.34 |
| Image Generation (VE, PC) | CelebA 64x64 | 8.28 |
Business Applications
This table provides a quick overview of how STF can streamline various business operations relating to image generation.
| Tasks | Business Use Cases | Examples |
| Image Generation | CIFAR-10 | 1.9 |
Model Features
Here are some technical model features of STF, as described in the paper "Stable Target Field for Reduced Variance Score Estimation in Diffusion Models":
Generalized denoising score-matching objective
STF is a generalized version of the denoising score-matching objective. It includes an additional reference batch of examples for calculating weighted conditional scores as targets.
Self-normalized importance sampling
STF uses self-normalized importance sampling to aggregate the contribution of each example in the reference batch. This helps to reduce the variance of training targets in the intermediate regime.
Bias reduction and trace-of-covariance
STF introduces some bias, but the bias and trace-of-covariance of the STF training targets shrink to zero as the size of the reference batch increases.
Stability and training speed
STF enhances the stability of converged score-based models on CIFAR-10 and CelebA and helps avoid generating noisy images. It also accelerates the training of score-based models while obtaining comparable or better FID scores.
Theoretical guarantees
The paper provides theoretical guarantees that the proposed STF objective is asymptotically unbiased and reduces the trace-of-covariance of the training targets by a factor about the reference batch size in the intermediate phase under mild conditions.
Model Tasks
Denoising
Denoising is a common NLP task that involves removing noise from text data. This can include correcting spelling and grammar errors, removing unwanted characters or symbols, and filtering out irrelevant information. Denoising can be used in various business applications, such as sentiment analysis, customer feedback analysis, and content moderation.
Image generation
Image generation is an NLP task that involves generating text descriptions of images. This can be useful for automatically generating captions for social media posts or for creating metadata for large collections of images. Image generation can be used in various business applications, such as e-commerce, travel and tourism, and digital marketing.
Fine-tuning
The authors haven't explicitly mentioned about the fine-tuning methods in the research paper. The fine-tuning methods will be updated here soon.
Benchmark Results
Benchmarking is an important process to evaluate the performance of any language model, including STF. The key results are;
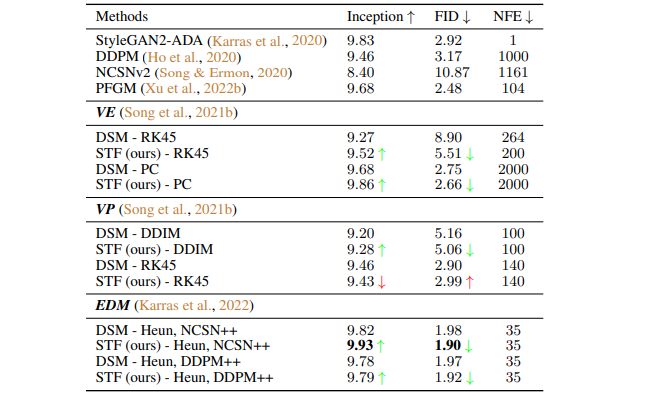
CIFAR-10 sample quality (FID, Inception) and number of function evaluation (NFE).
Sample Codes
An example code to train STF on a GPU using TensorFlow
import tensorflow as tf
from stf import STF
# Define hyperparameters
learning_rate = 0.001
batch_size = 32
num_epochs = 50
# Load dataset
train_dataset = ...
# Define neural network architecture
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu', input_shape=(input_shape,)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(output_shape, activation='softmax')
])
# Define STF objective function
stf = STF(reference_batch_size=256, temperature=0.1)
# Define optimizer
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate)
# Compile model
model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=stf.loss)
# Train model on GPU
with tf.device('/GPU:0'):
history = model.fit(train_dataset, epochs=num_epochs, batch_size=batch_size)
# Evaluate model on validation dataset
val_dataset = ...
metrics = model.evaluate(val_dataset)
# Generate new samples
generated_samples = model.predict(...)
Model Limitations
-
Although the original EDM repository includes additional datasets such as FFHQ, AFHQv2, and ImageNet-64, the researchers did not test the performance of STF on these datasets due to computational constraints. However, they believe that the STF technique can consistently enhance the performance of generative models across different datasets.
Other LLMs

PFGM++
PFGM++ is a family of physics-inspired generative models that embeds trajectories for N dimensional data in N+D dimensional space using a simple scalar norm of additional variables.
Read More


MDT-XL2
MDT proposes a mask latent modeling scheme for transformer-based DPMs to improve contextual and relation learning among semantics in an image.
Read More


Stable Diffusion
An image synthesis model called Stable Diffusion produces high-quality results without the computational requirements of autoregressive transformers.
Read More